Investing in Stocks: A Beginner's Guide

Introduction to Stock Investing
Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time. This beginner's guide will introduce you to the basics of stock investing, helping you understand how to get started and what to consider along the way.
Understanding Stocks
What are Stocks?

Stocks represent ownership shares in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a part-owner of that company and can benefit from its growth and profits.
Types of Stocks

There are two main types of stocks: common stocks and preferred stocks. Common stocks provide voting rights and dividends, while preferred stocks offer fixed dividends and priority over common stocks in case of liquidation.
Getting Started with Stock Investing
1. Setting Financial Goals

Before investing, it's important to set clear financial goals. Determine what you want to achieve with your investments, whether it's saving for retirement, buying a house, or generating passive income.
2. Understanding Risk Tolerance

Assess your risk tolerance by considering your financial situation, investment goals, and comfort level with market fluctuations. This will help you choose the right stocks and investment strategies.
3. Researching Stocks

Conduct thorough research before investing in any stock. Look at the company's financial statements, market position, management team, and growth potential. Understanding the business model and industry trends is also crucial.
4. Diversifying Your Portfolio

Diversification involves spreading your investments across different stocks, sectors, and asset classes to reduce risk. A diversified portfolio can help mitigate losses and enhance returns.
Key Concepts in Stock Investing
1. Market Capitalization

Market capitalization, or market cap, is the total value of a company's outstanding shares of stock. It's calculated by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. Companies are categorized as large-cap, mid-cap, or small-cap based on their market cap.
2. Dividend Yield

Dividend yield is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its stock price. It's a useful metric for investors seeking regular income from their investments.
3. Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)
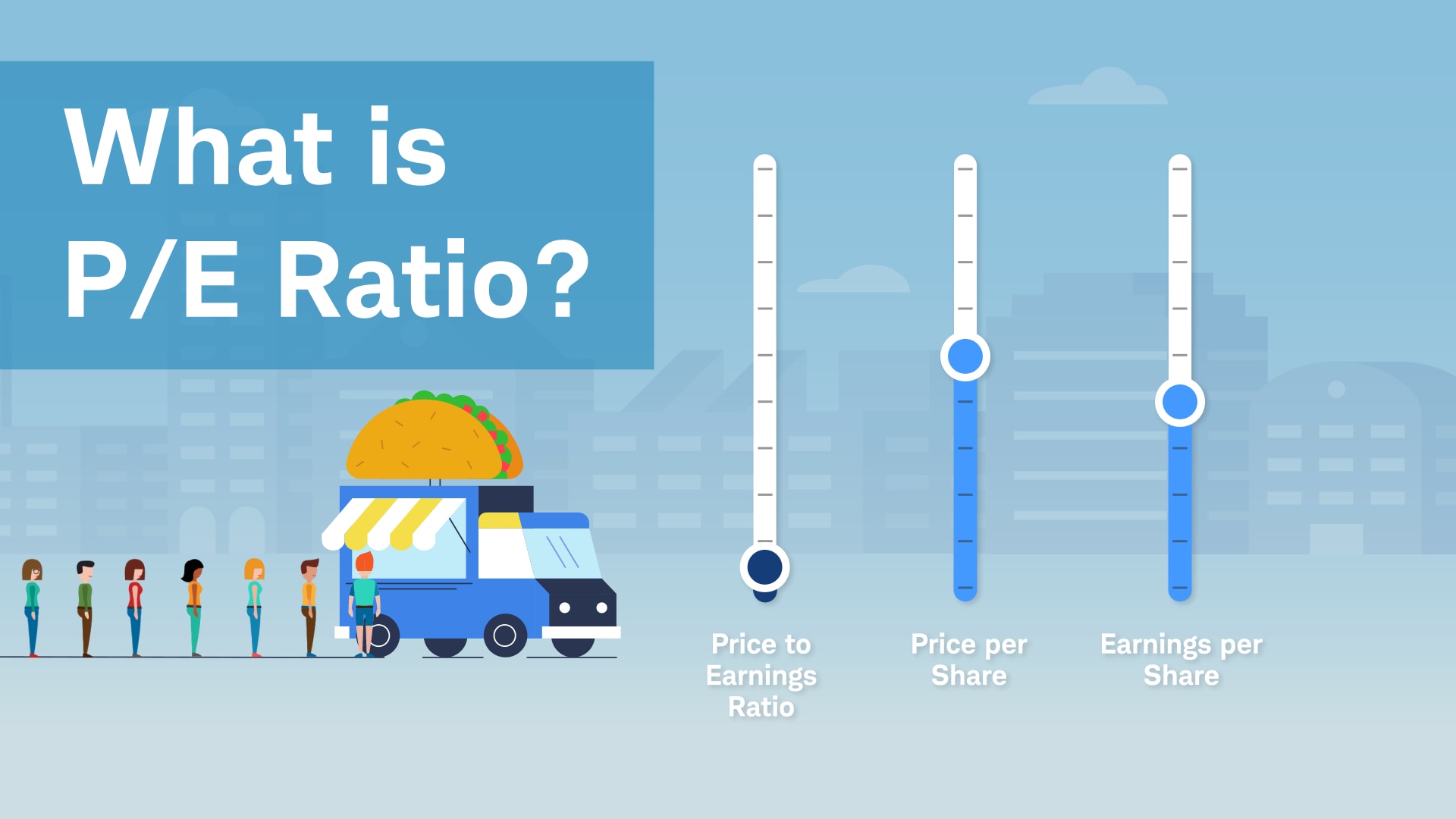
The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio measures a company's current share price relative to its per-share earnings. It's used to evaluate whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly valued compared to its earnings.
4. Earnings Per Share (EPS)

Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. It's a key indicator of a company's profitability and is often used by investors to gauge financial health.
Conclusion
Investing in stocks can be a rewarding way to build wealth, but it requires knowledge, research, and careful planning. By understanding the basics and key concepts of stock investing, you can make informed decisions and set yourself up for long-term success.
Keep learning and stay informed about market trends and economic factors that can impact your investments. Happy investing!